National Formosa University (NFU) Develops Virtual Table Tennis Coaching System and Helps Athletes with Sports Technology
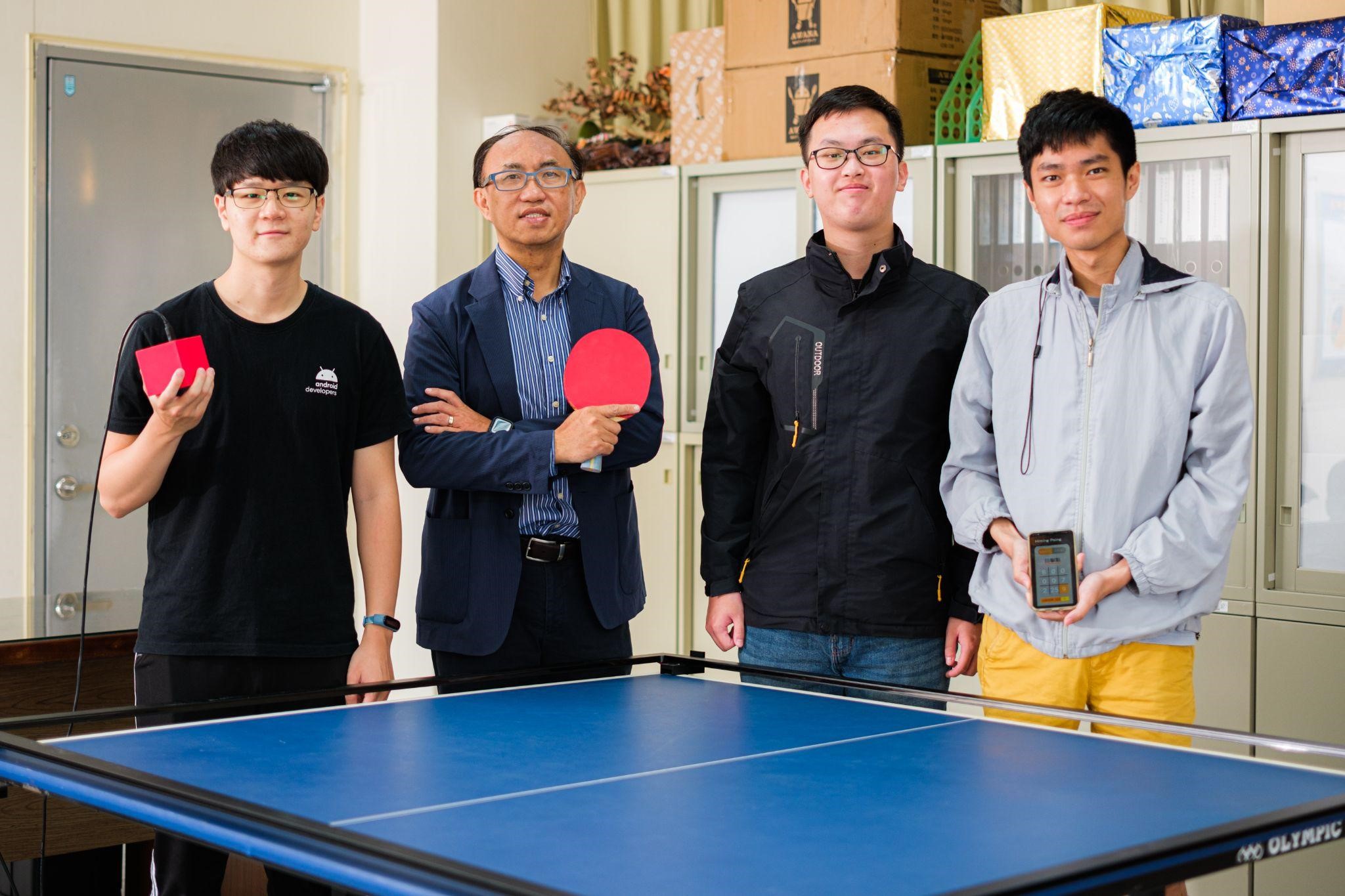
In recent years, the development of sports tech has become increasingly popular in many different kinds of sports, and table tennis is one of them. Therefore, a number of R&D teams have set their sights on this field and made various endeavors. Under such trends, this interview with the National Formosa University (NFU) team will offer an insight into the world of sports tech. The NFU sports tech team is led by Dr. Yung-Hoh Sheu, Dean of the College of Electrical and Computer Engineering, and has developed a "virtual table tennis coaching system" which integrates a variety of equipment and components.
For a table tennis athlete, skills and reaction speed are two critical factors. The reaction of professional athletes in a game is always in split seconds or even milliseconds. In this regard, the virtual table tennis coaching system can help users train their hitting skills, improve reaction speed, and at the same time provide a large amount of data of records and analyses. With the aid of technology, athletes can identify blind spots that are previously difficult to detect in traditional training models, thereby enhancing training efficiency and effectiveness.
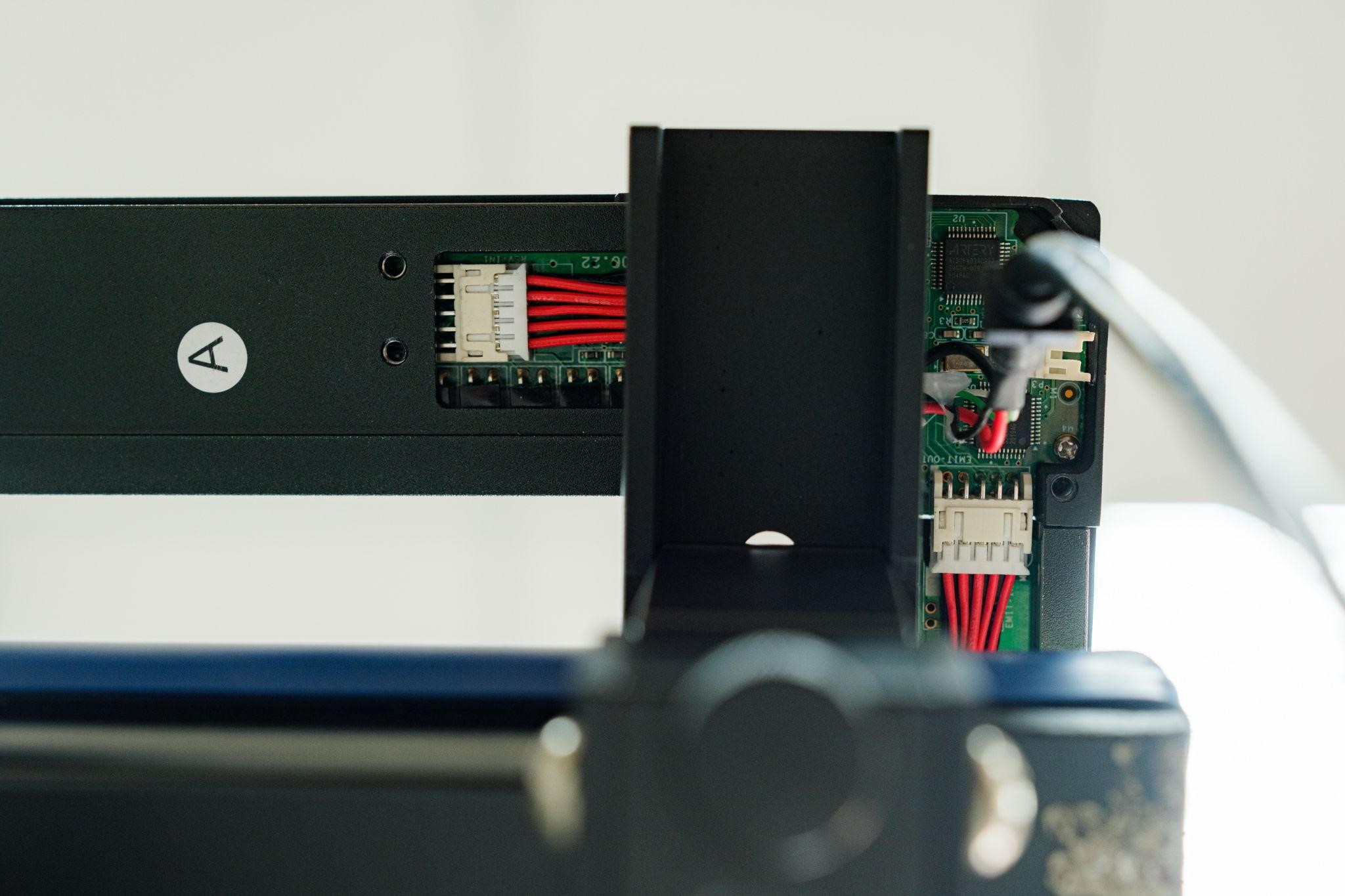
The core of this system is composed of a large infrared sensor module. Its operating principle is the same as that of a large electronic whiteboard. Around the sensor module which looks like a window frame, a total of 128 infrared sensing components are installed to detect the landing position of the ball on the table. These data will then be transmitted to the circuit control box and then the mobile device via Bluetooth, and users can see such data displayed on the device screen in no time.
Although the operating principle is not complicated, the difficulty encountered during implementation was that ping-pong balls are small in size and move very fast, making it difficult to render accurate detection. Thus, the know-how of the system lies in how well the system can control the infrared sensors with divergent sensing range, and how it can utilize the captured signals to calculate the specific landing position. However, controlling the landing position of a hit is actually not difficult for professional players, as it is only a basic training item. For them, the focus of their training is about how well and quickly they can react in the game, so the challenge of the system is how to create a training model that is realistic and effective.
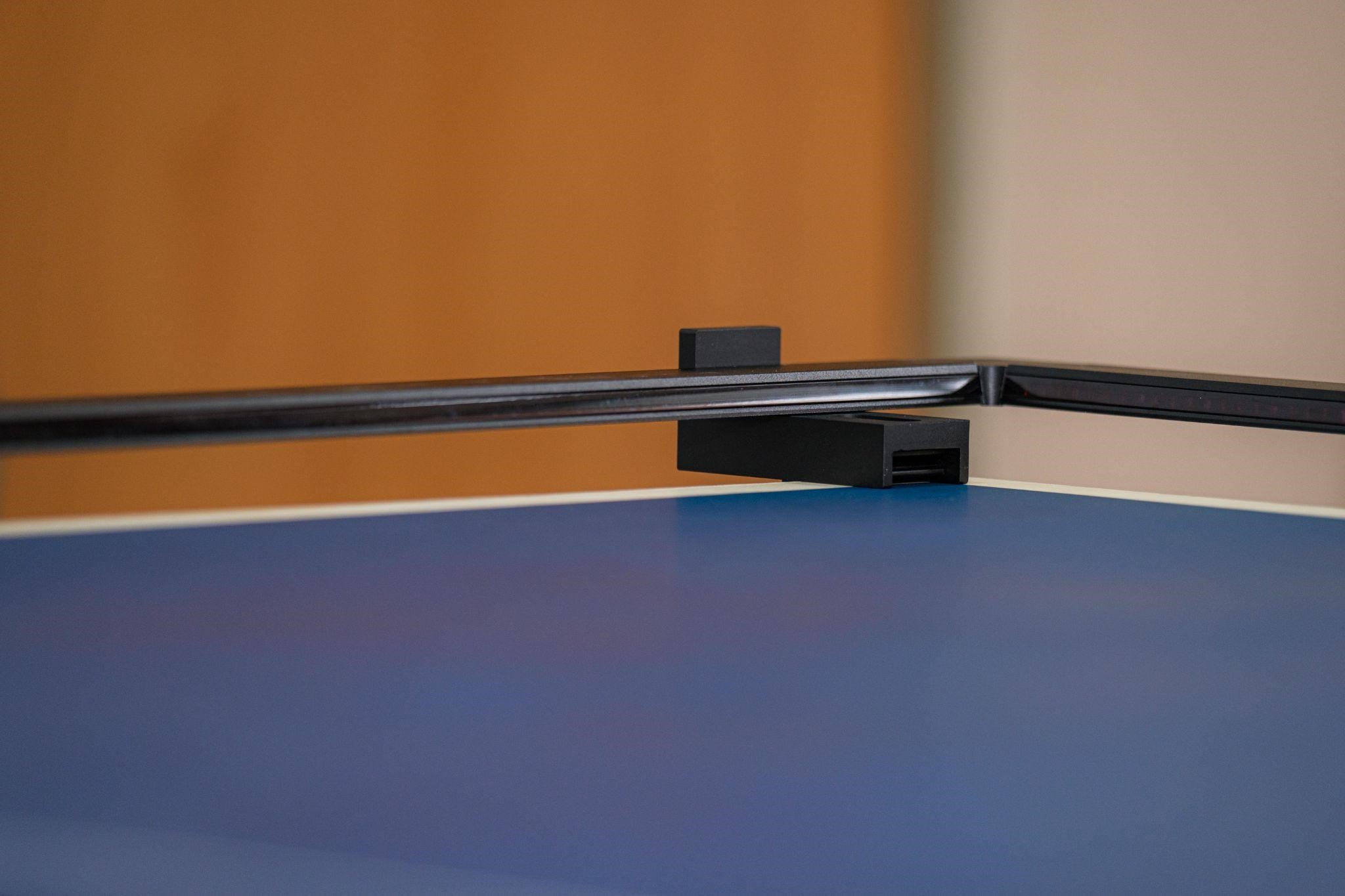
Table tennis is a sport that requires a refined set of skills. In the virtual table tennis coaching system designed by Dr. Yung-Hoh Sheu's team, in addition to the landing position detection function developed in collaboration with the IoT Service Hub, there are also a smart table tennis racket and a ball machine which can simulate a game with real players at any time. First, by installing pressure sensor, gyroscope, and acceleration sensor on the racket, the system can record the player's hitting trajectory, whether the racket surface is effectively hitting the ball, and whether the player can maintain stability during the game. All these data will then be analyzed. After a large amount of data is collected, the team also started to develop a ball machine that can better simulate a real player to replace the traditional ball machine that can only serve balls in a repeated, fixed path. With the new-generation ball machine providing instant changes in the balls it serves, players' training needs are better satisfied.
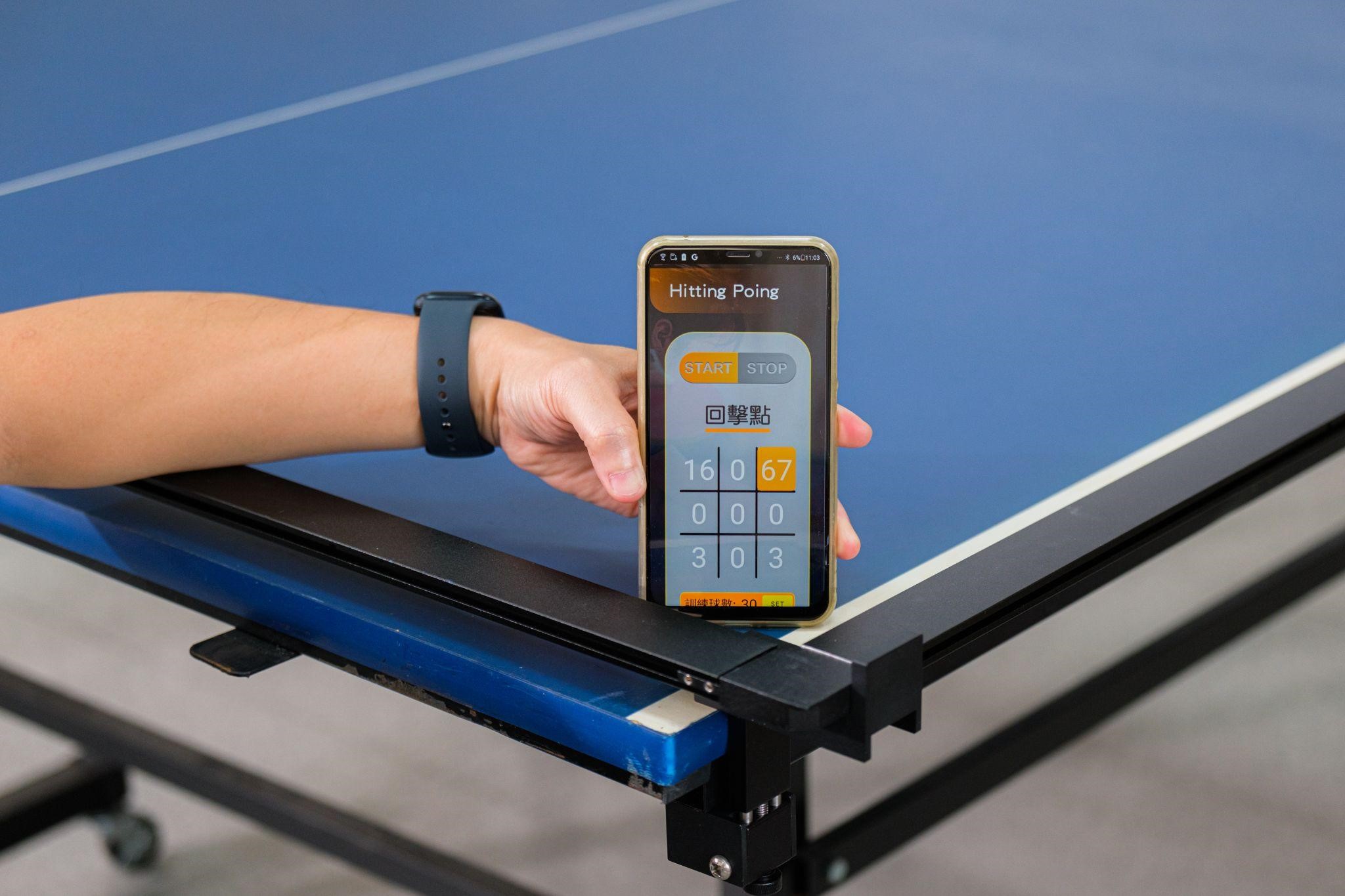

During the design process, Dr. Sheu integrated multiple devices to build a complete training system for the players. By sending information back to the system, the coach can analyze the players' weaknesses and proficiency levels and then generate a tailored training program to cater to individual player's specific needs based on the results of data analysis.

Since the virtual table tennis coaching system contains multiple components and its development requirements are complex, the NFU team cooperated with the IoT Service Hub to gain an in-depth understanding of the development status and difficulties. The IoT Service Hub then helped the team find suitable partners through its extensive network. For example, the exterior and mechanism design of the infrared touch frame stabilizer and circuit control box was accomplished by LEXIN OPTO, a long-term partner of the IoT Service Hub. In the system's subsequent development, the NFU team will continue to work with the IoT Service Hub so as to accelerate development and secure more resources and application opportunities.
According to Dr. Sheu, the virtual table tennis coaching system has a wide range of applications. It can not only allow professional players to train anytime, but can also be extended to gym or sports center settings, where machines of simpler specifications can be used for daily training and exercise purposes. In order to meet such needs, the team is now actively integrating VR and AR technologies to design more scenarios suitable for users of all ages. In the future, the system is even expected to be utilized in long-term care settings as it can significantly help patients or elders with rehabilitation needs Of course, there is still a lot of room for development in the virtual table tennis coaching system. In the future, upgrades can be made to make the system detect the position and speed of the ball more accurately, thereby providing the athletes with better training in a more scientific way and help them enhance their skills more effectively.



